Imagine this: you inherit a sizable sum from a loved one. Joy and gratitude likely wash over you. But in many countries, this inheritance comes with a financial sting – inheritance tax. India, however, stands out as a nation without such a levy. Should this change? Let’s delve into the potential advantages and disadvantages of implementing an inheritance tax system in India, drawing comparisons to how other countries handle this complex issue.
The Allure of Equality: Redistribution and Social Programs
One of the most compelling arguments for inheritance tax lies in its potential to promote social equality. In India, where wealth concentration is a growing concern, a well-designed inheritance tax system could be a powerful tool for redistribution.
Learning from Global Leaders:
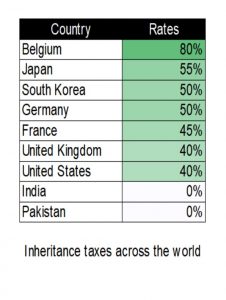
Look at countries like France, where inheritances exceeding a certain threshold can be taxed up to 60%. The UK employs a similar system, with rates reaching 40%. Both utilize progressive tax structures – the more you inherit, the higher the tax percentage. This ensures that only those inheriting vast sums face a significant tax, minimizing the impact on middle-class families.
Imagine this scenario: you inherit a modest sum from your parents. Under a well-designed system in India, you might not face any inheritance tax at all. However, if you inherit a massive fortune from a distant relative, a portion of that inheritance could be directed towards social programs. This could translate to better schools, improved healthcare facilities, and more efficient public services, ultimately benefiting a broader segment of society.
Potential Impact on Social Mobility:
Inheritance tax can also act as a catalyst for social mobility. Consider this: if immense wealth is readily inherited, future generations may lack the drive to pursue careers or develop new businesses. A well-structured inheritance tax system, particularly on larger estates, could incentivize hard work and innovation. This could pave the way for a society where success is based on individual talent and effort, not just on fortunate birthrights.
Funding a Brighter Future:
The revenue generated from inheritance taxes can be a significant source of funding for crucial social programs. In India, where investments in education, healthcare, and infrastructure are needed, inheritance tax can provide a much-needed boost. This can empower future generations and contribute to India’s long-term development trajectory.
Addressing Concerns: Striking a Balance
While the potential benefits of inheritance tax are undeniable, some concerns need careful consideration.
- Discouraging Investment: Opponents argue that high inheritance tax rates could discourage wealthy individuals from investing or creating businesses. This could potentially stifle economic growth in India, where entrepreneurship plays a vital role. Finding the right balance is crucial – a system with exemptions for productive investments and smaller estates could mitigate this concern.
Imagine you’re a successful entrepreneur. A well-designed inheritance tax system could allow you to leave a significant portion of your wealth to your children without hindering your business ventures. Exemptions for reinvested profits or business assets could incentivize continued economic growth.
- Administrative Burden: Implementing and enforcing a new tax system can be complex and expensive. India would need to ensure a robust tax administration with a strong legal framework to prevent evasion and ensure smooth operation. Lessons can be learned from countries like the United States, where complex inheritance tax structures have created loopholes and administrative challenges.
A Global Perspective: Examples and Best Practices
Look at developed nations like the UK and Germany. They offer tax-free thresholds for smaller estates. This protects middle-class families from undue burden. India could adopt a similar approach, focusing on taxing only large inheritances.
Many developed countries have also learned from past mistakes. Japan, for instance, has intricate tax laws that have led to practices like “gifting while alive” to circumvent inheritance tax. India could implement clear regulations and robust enforcement measures to minimize such practices.
Beyond the Numbers: The Societal Impact
The debate surrounding inheritance tax extends beyond economic considerations. It touches upon deeply rooted cultural values and societal aspirations.
- Family Legacy and Continuity: In India, where family businesses play a significant role in the economy, some argue that inheritance tax could disrupt generational continuity and weaken established businesses. However, a well-designed system with exemptions for productive businesses could address this concern.
Imagine you’re part of a family-owned business. With careful planning and strategic asset allocation, you could ensure the smooth transfer of your business to the next generation, even with an inheritance tax in place.
- Cultural Considerations: The concept of inheritance is often intertwined with the concept of familial responsibility in Indian culture. Opponents argue that inheritance tax could undermine this tradition and create friction within families.
The decision to implement inheritance tax in India is a complex one. While the current system benefits inheritors, a well-structured inheritance tax could promote social mobility and contribute to India’s future development. However, striking a balance is crucial to avoid discouraging investment and creating administrative burdens. Open discussions and careful consideration of the global landscape are essential before India decides whether to adopt this potentially transformative tax system.